5-Amino-1MQ (60 Capsules)
$200.00
Out of stock
Each capsule contains 50mg 5-Amino 1MQ
5-amino-1MQ is a small molecule that blocks the activity of the enzyme called nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT). NNMT is a very important component in metabolism and energy and is predominantly active in fat tissue. By blocking NNMT, 5-amino-1MQ stimulates an increase in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a cofactor that is central to cellular metabolism, thereby increasing metabolic rate and activating a gene called sirtuin-1 (SIRT1). SIRT1 is also known as the “longevity gene” because of its role in reducing the risk of diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, atherosclerosis and other forms of cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, liver disease, neurodegeneration, and cancer. According to research in mice given 5-amino-1MQ showed a 7% reduction in body mass without any changes in food intake, compared to controls. Research has shown that decreasing NNMT may help shrink fat cells and reduce the size of fat deposits.
Product description
5-Amino-1MQ Overview
5-amino-1MQ (5-amino-1methylquinolinium) an analogue of methylquinolinium, is a short peptide inhibitor of cytosolic nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT). The NNMT enzyme has been linked to both obesity and type 2 diabetes and is known to play a role in energy homeostasis within the cell. Inhibiting NNMT leads to significant weight loss, decreased fat mass and fat cell (adipocyte) size, and lower plasma cholesterol and glucose levels. 5-amino-1MQ and other methylquinolinium derivatives are under active investigation as potential treatments for obesity and diabetes. It also appears that inhibition of NNMT can activate stem cells and improve regenerative capacity in skeletal muscle
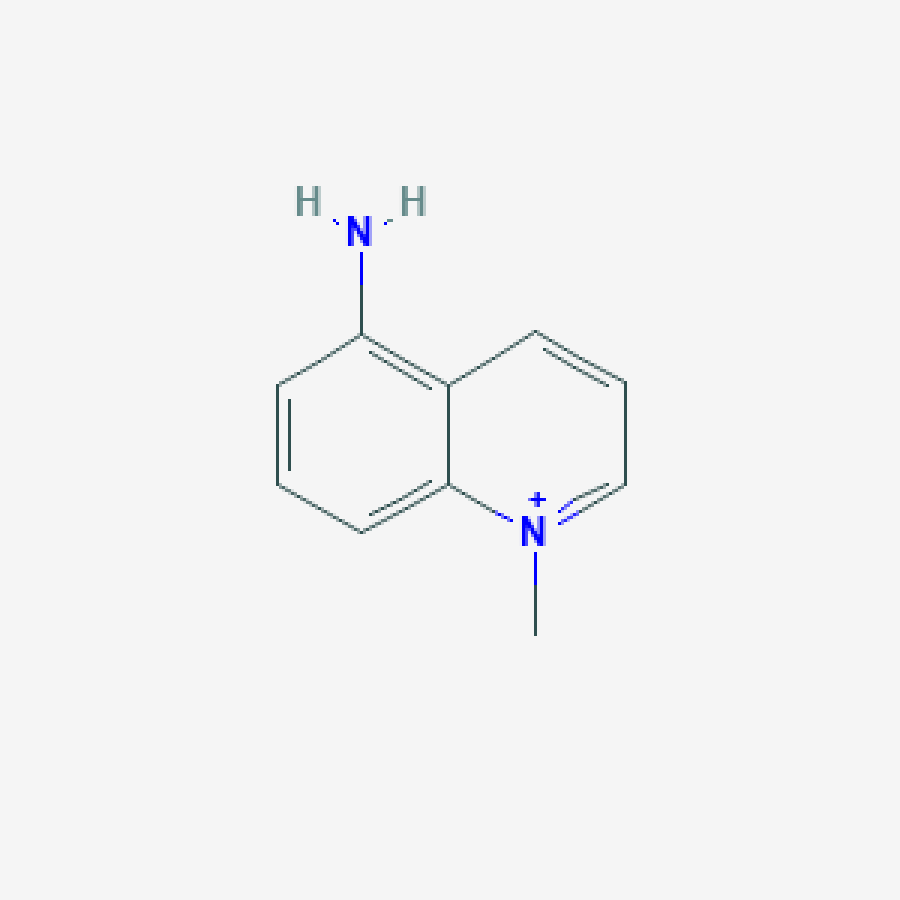
5-Amino-1MQ Structure
Molecular Formula: C10H11N2
Molecular Weight: 159.21 g/mol
PubChem CID: 950107
CAS Number: 42464-96-0
Synonyms: 5-amino-1-methylquinolinium
5-Amino-1MQ Research
Obesity
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase is a cytosolic enzyme found in many cells throughout the body, but is most abundant in liver and fat cells. Research in mice shows that high levels of NNMT are associated with decreased levels of the sugar transporter GLUT4. GLUT4, which is primarily in striated muscle (skeletal and cardiac) and fat cells, is heavily linked to blood sugar levels and the development of diabetes. In rodent studies, mice that produce high levels of GLUT4 are insulin sensitive and relatively resistant to the development of type 2 diabetes while mice with low GLUT4 levels demonstrate profound insulin resistance. In fact, GLUT4 has been linked to basal metabolic rate and the concepts of fast and slow metabolism. Individuals with naturally high levels of GLUT4 have “faster metabolism” than those with low levels of GLUT4 and burn more calories as a result. It is also true that production of the
transporter is stimulated by exercise, explaining why exercise can help to combat weight loss, elevated blood sugar levels, and insulin resistance. As it turns out, GLUT4 and NNMT are closely linked to one another and to basal metabolism in mammals [1]. According to Dr. Barbara Kahn of Harvard Medical School, the connection between GLUT4 and NNMT is what first led to the investigation of the latter enzyme as a potential target in the treatment of diabetes and obesity. High levels of NNMT are often found in the fat cells of animals with insulin resistance. Manipulating this gene helps to counteract insulin esistance and thus diabetes. It also has a profound effect on weight and obesity. Human metabolism, and indeed all animal metabolism is highly efficient, making the most use out of a limited number of calories. Unfortunately, this very efficiency may be the mechanism underlying our penchants for obesity in the setting of excess calorie intake.
Reducing the efficiency of human metabolism, causing the body to essentially waste calories, has long been a holy grail of medicine as it works to combat the growing obesity epidemic. NNMT and its interactions with GLUT4 may be the link that scientists have been searching for. [2], [3].
In the most basic sense, NNMT slows how quickly the body utilizes calories thereby leaving them
available for storage in fat or glycogen. Decreased NNMT levels decrease the conversion of
nicotinic acid (NA) into 1-methylnicotinamide (1-MNA). This process has two effects on
metabolism as follows.
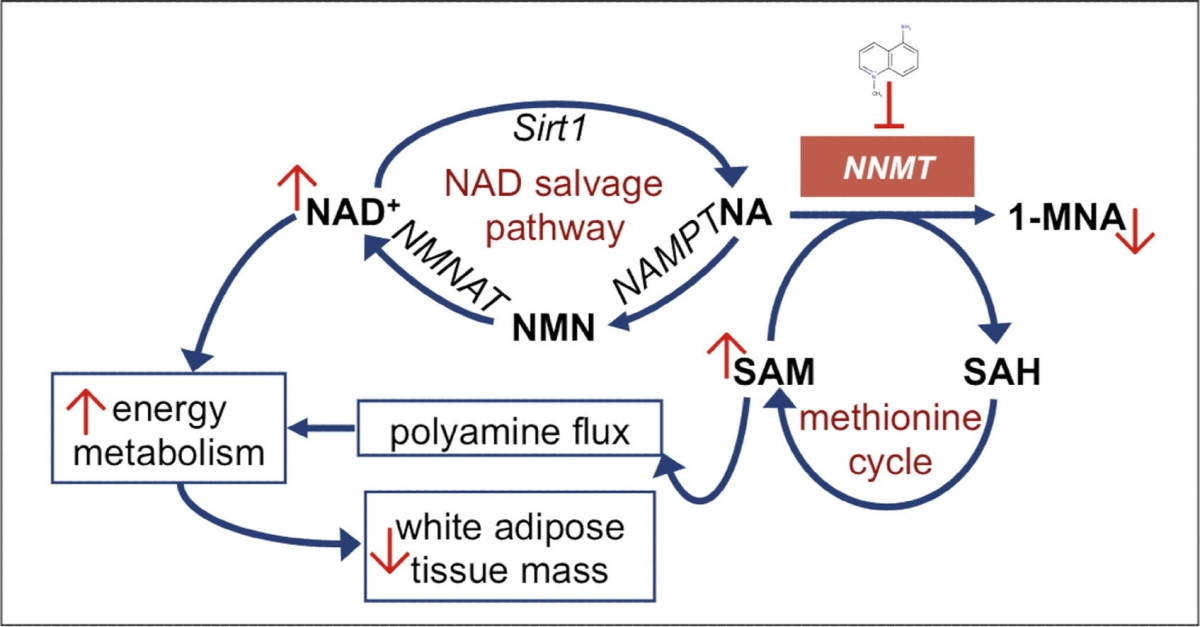
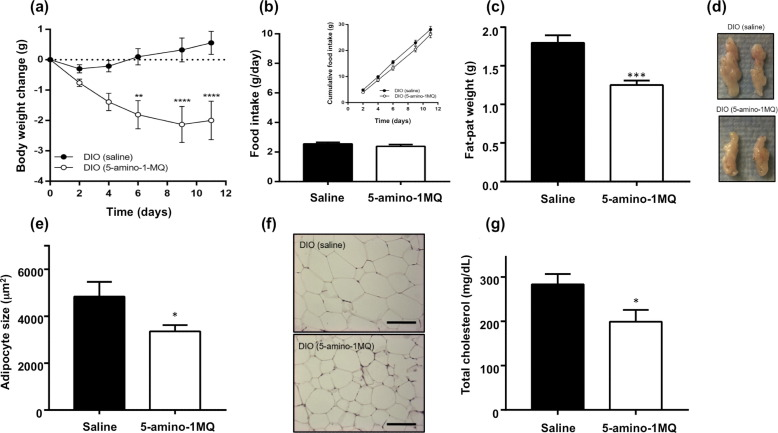
So the net result of administering an NNMT blocker like 5-amino-1MQ is an increase in energy burning and a decrease in energy storage. When this is coupled with the fact that decreased NNMT levels also increases GLUT4 transporter expression, you have a recipe for improve glucose clearance from the blood and then direct disposition of that glucose when it is burned. The results are decreased need for insulin, decreased insulin resistance, decreased fat production, and increased energy metabolism. Studies in mice over just 10 days of 5-amino-1MQ administration reveal a 7% reduction in rate and a 30% reduction in fat mass. In addition, blood cholesterol levels in treated mice are equal to those of non-obese mice. Remarkably, these changes occur without any alteration in food consumption [5]. Mice given 5-amino-1MQ show a 7% reduction in body mass over just 10 days, without any changes in food intake, compared to controls:
More recent evidence suggests that the benefit of 5-amino-1MQ may extend beyond its ability to downregulate NNMT and thus increase inefficient metabolism and GLUT4 expression. Research in mice suggests that by boosting GLUT4 expression, 5-amino-1MQ may alter the way fat cells work, leading them to produce an alternative class of lipids that have anti-diabetic and antiinflammatory effects. This class of lipids, known as PAHSAs (palmitic acid esters of hydroxystearic acids), can reduce insulin resistance on their own and reduce inflammation leading to improved risk profiles for events like heart attack and stroke [6]. Those this aspect of 5-amino1MQ is relatively new, it hints at an extended benefits profile for this already remarkable molecule.
5-Amino-1MQ and Muscle Function
The impact of 5-amino-1MQ on skeletal muscle is multifaceted. Much like in adipose tissue, the presence of 5-amino-1MQ in muscle promotes the production of the GLUT4 receptor and boosts the inefficiency of metabolism leading to increased energy burn. Recent research in mice, however, suggests that inhibiting NNMT in any way, including with 5-amino-1MQ, may actually boost muscle repair by stimulating stem cells. Research in 24-month-old mice (old for mice) reveals that those treated with an NNMT inhibitor experience substantial stem cell activation in muscle tissue, following injury, compared to controls. These mice exhibit myofibers that are 2-fold larger in cross section and have greater contractile strength. In fact, mice treated with NNMT inhibitors have 70% more contractile force in healed muscle than control mice [7]. The benefits of boosting muscle stem cell production go well beyond
simply accelerating rates of repair following injury. Stimulating stem cells could help elderly people maintain their independence for much longer. By improving mobility and reducing the risk of things like falls, NNMT inhibitors could substantially improve quality of life and levels of independent living among older adults.There is also evidence that increased NNMT expression is a common feature of muscle wasting disorders such as Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and that reducing NNMT levels may help to alleviate the symptoms of some of these conditions [8]. This, again, is tied in to the ability of NNMT to inhibit stem cell growth and division. By reducing NNMT levels, compounds like 5-amino-1MQ may provide benefit in a variety of muscle-wasting conditions. The exact effects of NNMT inhibition on muscle function are not fully understood, but another component appears to relate to NAD+ levels. ecall that NNMT inhibition results in increased levels of NAD+. By replenishing NAD+ levels via NNMT inhibition, compounds like 5-amino-1MQ have been shown to improve muscle function, heart pathology, and DMD in animal models. It appears that improvement in mitochondrial function combined with decreases in inflammation and fibrosis, all related to increases in NAD+ levels, are the main drivers of these benefits [9].
A Possible Role for 5-Amino-1MQ in Cognition
NAD+ is a critical compound in brain energy homeostasis. Depletion of NAD+ has been linked to a number of cognitive conditions, but is known to impact communication at the synaptic junction of neurons and at the neuromuscular junction where nerves connect to muscle tissue. Research in mice suggests that decreases in NAD+ levels can reduce synaptic transmission, impair muscle function, and impact overall cognitive function [10]. Though 5-amino-1MQ has not been specifically tested in this setting, there is good reason to believe that the compound will have the same effect on NAD+ levels in the brain as it has elsewhere. This means that it could be used not just as a treatment for cognitive dysfunction, but as a potential nootropic to boost cognitive function in the average individual. Whether this bears out in research remains to be seen, but there is active interest in the potential cognitive benefits of 5-amino-1MQ.
NNMT and Cancer
There is significant research to suggest that NNMT expression is increased in gastric cancers of all types as well as pancreatic cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and bladder cancer. Mice without the NNMT gene so resistance to the development of these cancers, suggesting a causal role for NNMT. Though the research is still in progress, there is some speculation that inhibition NNMT may be a way to both treat and prevent certain types of cancer or, at the very least, reduce how aggressive certain cancer are[8]. It remains to be seen whether 5-amino-1MQ, by reducing NNMT function, will have any effect on the various cancers mentioned.
5-Amino-1MQ Summary
5-amino-1MQ is a small, membrane permeable analogue of naturally occurring methylquinolinium. It has been shown, in animal models to inhibit expression of the enzyme nicotinamide Nmethyltransferase. NNMT is an important component of cellular energy metabolism and has been linked heavily to weight control and insulin resistance. Studies show that inhibiting NNMT with 5-amino-1MQ can lead to weight reduction, resistance to diabetes, and improved plasma cholesterol levels. There is also good evidence to show that NNMT inhibition can help to regulate muscle and nerve cell function and there is some hope that compounds like 5-amino-1MQ may play a role in the treatment of conditions like muscular dystrophy and the muscle wasting that results from age. Reductions in levels of NNMT have been linked to reduced aggressiveness in several different varieties of cancer. 5-amino-1MQ exhibits minimal side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. 5-amino-1MQ for sale at Peptide Sciences is limited to educational and scientific research only, not for human consumption. Only buy 5-amino-1MQ if you are a licensed researcher.
Article Author
The above literature was researched, edited and organized by Dr. E. Logan, M.D. Dr. E. Logan holds a doctorate degree from Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and a B.S. in molecular biology.
Scientific Journal Author
Barbara B. Kahn is chief of the Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and the George Richards Minot Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. She is an internationally recognized scientist in the area of obesity and type 2 diabetes, and her lab investigates the molecular mechanisms underlying these conditions, including the regulation of insulin action, food intake, and energy balance. Kahn received BA and MD degrees from Stanford University and an MS from the University of California at Berkeley. After completing internal medicine training at the UC Davis Medical Center, she began her career in molecular research at the National Institutes of Health. Kahn has received numerous awards including the Outstanding Scientific including the Outstanding Scientific Achievement Achievement Award from the ward from the American Diabetes American Diabetes Association; Association; the H. C. Jacobaeus Prize from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and the Karolinska Institutet; the Charles H. Best Lectureship and Charles H. Best Lectureship and Award from the University of ward from the University of Toronto; and the Gerald D. oronto; and the Gerald D. Aurbach Aurbach Award Lecture from the Endocrine Society. Kahn was elected to the Institute of Medicine of the National Academies and is a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Barbara B. Kahn is being referenced as one of the leading scientists involved in the research and development of 5-Amino-1MQ. In no way is this doctor/scientist endorsing or advocating the purchase, sale, or use of this product for any reason. There is no affiliation or relationship, implied or otherwise, between Peptide Sciences and this doctor. The purpose of citing the doctor is to acknowledge, recognize, and credit the exhaustive research and development efforts conducted by the scientists studying this peptide. Barbara B. Kahn is listed in [2] and [6] under the referenced citations.
Reference
1
2
3
4
5
ALL ARTICLES ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMA AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE TION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR ARE FOR INFORMA INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCA AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in-vitro studies only. In-vitro studies (Latin: in glass) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.